Learn how to architect, orchestrate, and optimize a world-class AI coding workflow with Claude Code. This step-by-step system helps you code efficiently, with quality and scale in mind.
Why This Guide Exists
Claude Code is powerful, but without a strong workflow you risk:
- Wasting tokens
- Generating code that doesn’t match your architecture
- Losing alignment between product managers and engineers
- Overcomplicating projects instead of accelerating them
This guide shows a senior-level development workflow built around:
- Context engineering first
- Separation of concerns
- Self-correcting systems
- Spec-driven development
- Checkpoints and state management
Part 1 — Core Philosophy
Context Engineering First
Don’t dump your entire repo into context. Instead, use priming lanes:
/prime_spec → load specs only
/prime_schema → load DB schema
/prime_bug → load failing tests and diffs
Example audit function:
function auditContext(tokensIn: number, windowLimit: number) {
const pct = tokensIn / windowLimit;
if (pct > 0.5) return { action: "compress", strategy: "chunk+summarize" };
return { action: "ok" };
}
Separation of Concerns
Each agent handles one responsibility:
prd-writerfor PRDssystem-architectfor architecture plansui-designerfor wireframesfile-creatorfor atomic editsstagehand-expertfor user journeys
Self-Correcting Systems
Every code mutation should trigger automatic validation:
async function postMutation(changedPaths: string[], affectedRoutes: string[]) {
await validateSupabase(); // Schema guard
const report = await runPlaywrightChecks(affectedRoutes);
return report;
}
Spec-Driven Development
Start with a PRD, structure it with Spec Kit, then implement in phases.
Part 2 — Project Structure
project/
├── ai/
│ ├── CLAUDE.md # 45-line always-loaded guide
│ ├── MANIFEST.md # Goals + agents in play
│ ├── IMPLEMENTATION_PLAN.md # Tasks + checkpoints
│ ├── PROMPTS/ # System prompts for agents
│ ├── WORKFLOWS/ # Repeatable flow contracts
│ ├── MCP/ # Configs for Firecrawl, Playwright, Supabase
│ └── CONTEXT/ # Prime docs and focus areas
├── specs/
│ ├── product/ # Spec Kit YAMLs
│ └── tech/ # Architecture specs, ADRs
├── docs/scraped/ # Auto-loaded reference docs
├── apps/web/ # Bun + Next.js frontend
└── packages/ # Shared libraries
Part 3 — Agent Architecture
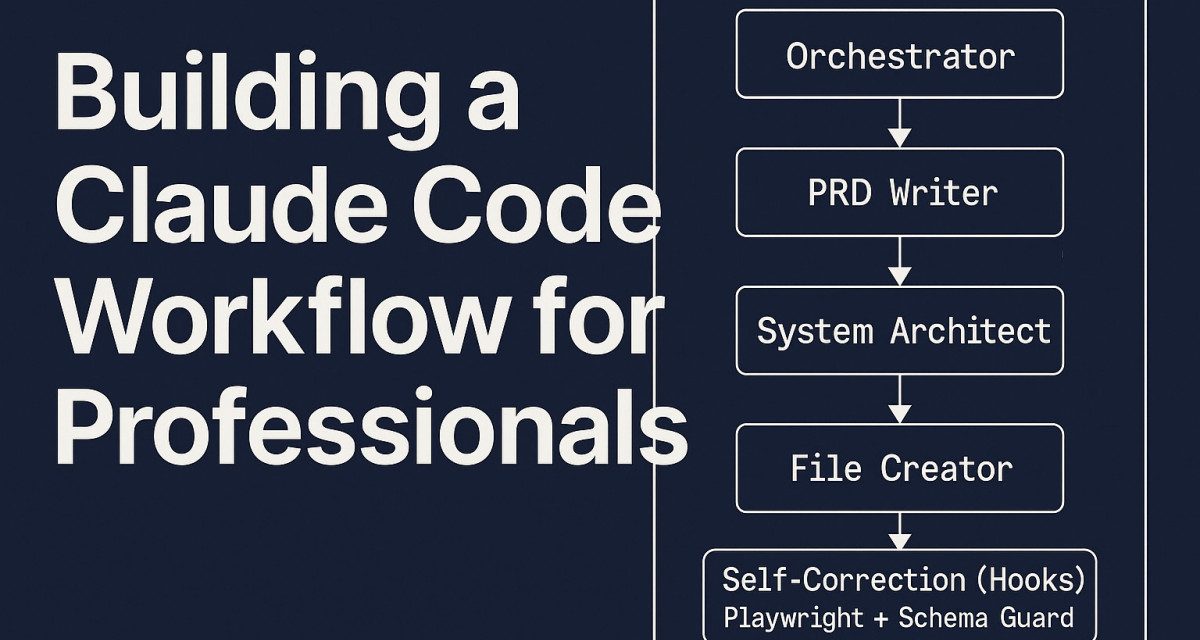
Orchestrator Pattern
orchestrator:
max_tools: 30
delegates_to:
- prd-writer
- system-architect
- ui-designer
- shadcn-expert
- react-typescript-specialist
- stagehand-expert
- nextjs-expert
- file-creator
- docs-scraper
Agent Flow Diagram
+------------------+
| Orchestrator |
+------------------+
|
v
+------------------+
| PRD Writer |
+------------------+
|
v
+------------------+
| System Architect |
+------------------+
|
v
+------------------+
| File Creator |
+------------------+
|
v
+---------------------------+
| Self-Correction (Hooks) |
| Playwright + Schema Guard |
+---------------------------+
Part 4 — Development Workflow
- Generate PRD
workflow:
- Initial Prompt → Iterate → Hand to prd-writer
- Output: spec.yml with personas, stories, KPIs
- Implement Features
bunx create-next-app apps/web
bun install
bun run dev
- Self-Correction Loop
await playwright.navigate(changedPages);
await playwright.screenshot();
const logs = await playwright.getConsoleLogs();
validateAgainstBackendSchema();
- Document Everything
- Feature docs list changed files
- ADRs updated automatically
- Hooks trigger doc updates
Part 5 — Testing & Validation
Visual Testing Workflow
1. Identify changes
- Review modified components
- List affected routes
2. Visual validation
- Navigate with Playwright MCP
- Capture screenshots
- Compare with baseline
3. Console monitoring
- Capture logs
- Validate API calls
Git Worktree A/B Testing
git worktree add ../feature-a feature-a
git worktree add ../feature-b feature-b
A judge agent can evaluate variations side-by-side.
Part 6 — State & Memory Management
- LangGraph: State objects + checkpoints
- LangSmith: Token tracking and compression metrics
- Pydantic: Runtime validation
- Graph databases: Relationship tracking
- Scratchpad + Memories: Separate short-term from long-term
Diagram:
+--------------------+
| Run State Obj |
+--------------------+
| goal, phase, inputs|
| artifacts, routes |
+--------------------+
|
v
+--------------------+
| LangGraph |
| (Checkpoints) |
+--------------------+
|
v
+--------------------+
| LangSmith (tokens) |
+--------------------+
Part 7 — Continuous Improvement
- Track
- Token usage per agent
- Compression effectiveness
- Self-correction success rates
- Optimize
- Remove unused tools
- Keep ≤30 tools per agent
- Reduce context with priming lanes
Quick Start Checklist
- Configure Bun + Next.js + shadcn
- Add CLAUDE.md (≤45 lines)
- Initialize Spec Kit in
specs/product/ - Configure Firecrawl + Playwright MCP
- Add MANIFEST.md and IMPLEMENTATION_PLAN.md
- Wire up post-mutation hooks
- Set up LangGraph + LangSmith tracking
- Create Git worktrees for A/B testing
Success Metrics
- Token efficiency: < 50% of window used
- Agent specialization: single domain per agent
- Self-correction rate: > 90%
- Documentation coverage: 100% of features
- Test coverage: visual + unit + E2E
Closing Thoughts
A Claude Code workflow should feel like working with a virtual senior engineering team. Product managers create structured PRDs, architects define plans, engineers implement code, QA runs automatically, and documentation stays in sync.
By following the steps in this guide—context engineering, agent specialization, hooks, specs, and orchestration—you can transform Claude Code into a professional-grade development environment.




Recent Comments